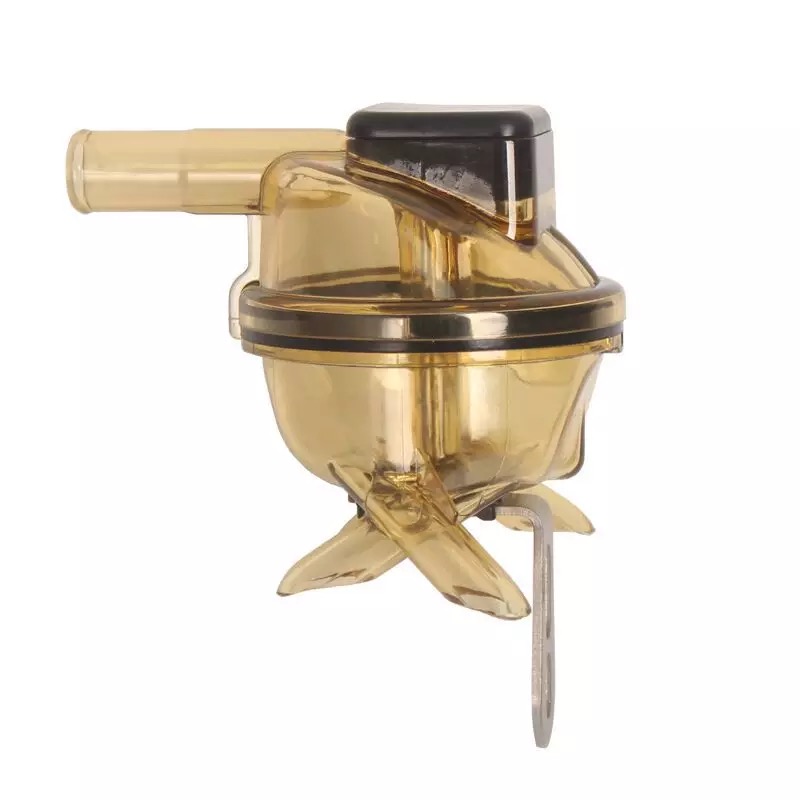

Polyphenylene sulfide (PSU) is a high-performance engineering plastic with excellent heat resistance, chemical resistance and mechanical strength. The processing process of making milk collectors from polyphenylene sulfide (PSU) material usually includes the following steps:
Material preparation: PSU pellets or powder are prepared for injection molding or extrusion molding. At this stage, any necessary additives can be added to meet the specific requirements of the product.
Injection molding or extrusion: PSU material is heated to the appropriate temperature and then molded through an injection molding or extrusion machine. Injection molding can be used to create complex-shaped parts, while extrusion is suitable for producing continuous lengths of product.
Forming: The material is passed through a mold to form the desired milk collector part. The cooling process ensures that the parts maintain their shape.
Machining and Shaping: Parts may require subsequent machining and shaping to ensure they meet design specifications, including the removal of any imperfections or excess material that may be present.
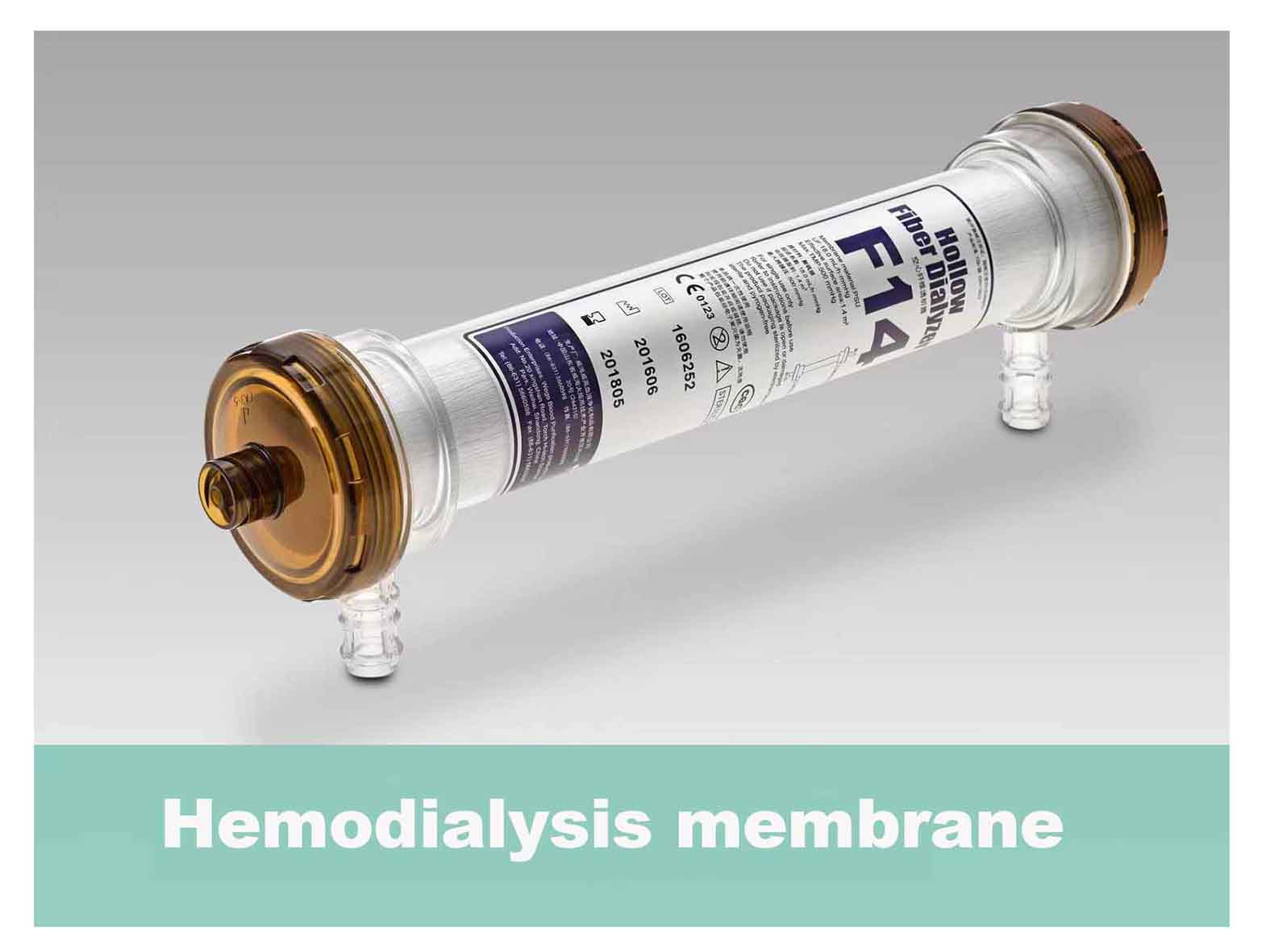
Using PSU materials to make hemodialyzers can conduct careful research and experiments on special projects or daily experiments and blood processing. PSU materials are also widely used in the current medical field.
Although PSU materials are biocompatible, hemodialyzers made of PSU still need to be tested for biocompatibility to prevent defects in the product during production and processing, and to ensure that the PSU material will not cause immune reactions in patients or Other adverse reactions.
In the production of hemodialyzers, the purity of the PSU material is crucial, and the purity of the material needs to be maintained to prevent impurities or additives from interfering with the dialysis process.
Medical supplies require high-temperature sterilization and sterilization. PSU has high thermal stability, which allows the hemodialysis membrane to withstand high-temperature sterilization or cleaning.